AI workflows today are no longer about clever prompts – they’re about building systems that work reliably under pressure. The key? Orchestration tools and architecture patterns. Whether you’re using n8n, LangGraph, or agent frameworks like CrewAI, the focus should be on designing workflows that are efficient, scalable, and resilient to failures.
Here’s what you need to know:
- Orchestration Tools: Choose based on your team’s needs:
- n8n: Drag-and-drop simplicity for quick automation.
- LangGraph: Code-first precision for developers.
- CrewAI: Role-based agent collaboration.
- Hybrid approaches: Combine visual tools with code for flexibility.
- Architecture Patterns:
- Sequential Flows: Step-by-step processes, good for linear tasks.
- Parallel Execution: Run tasks simultaneously to save time.
- Validation Loops: Refine outputs through cycles of testing.
- Human-in-the-Loop: Add manual approvals for critical decisions.
- Error Handling: Plan for failures with fallback strategies.
- Production Tips:
- Self-hosting vs. Cloud: Control data with self-hosting or simplify scaling with cloud.
- Cost Management: Understand token pricing and avoid runaway costs.
- Debugging: Use tools like LangSmith for observability and troubleshooting.
- Version Control: Track workflow changes to prevent disruptions.
Avoid these mistakes: Over-engineering simple tasks, neglecting error handling, ignoring performance metrics, and skipping safeguards for critical workflows.
Framework Categories for AI Workflow Design
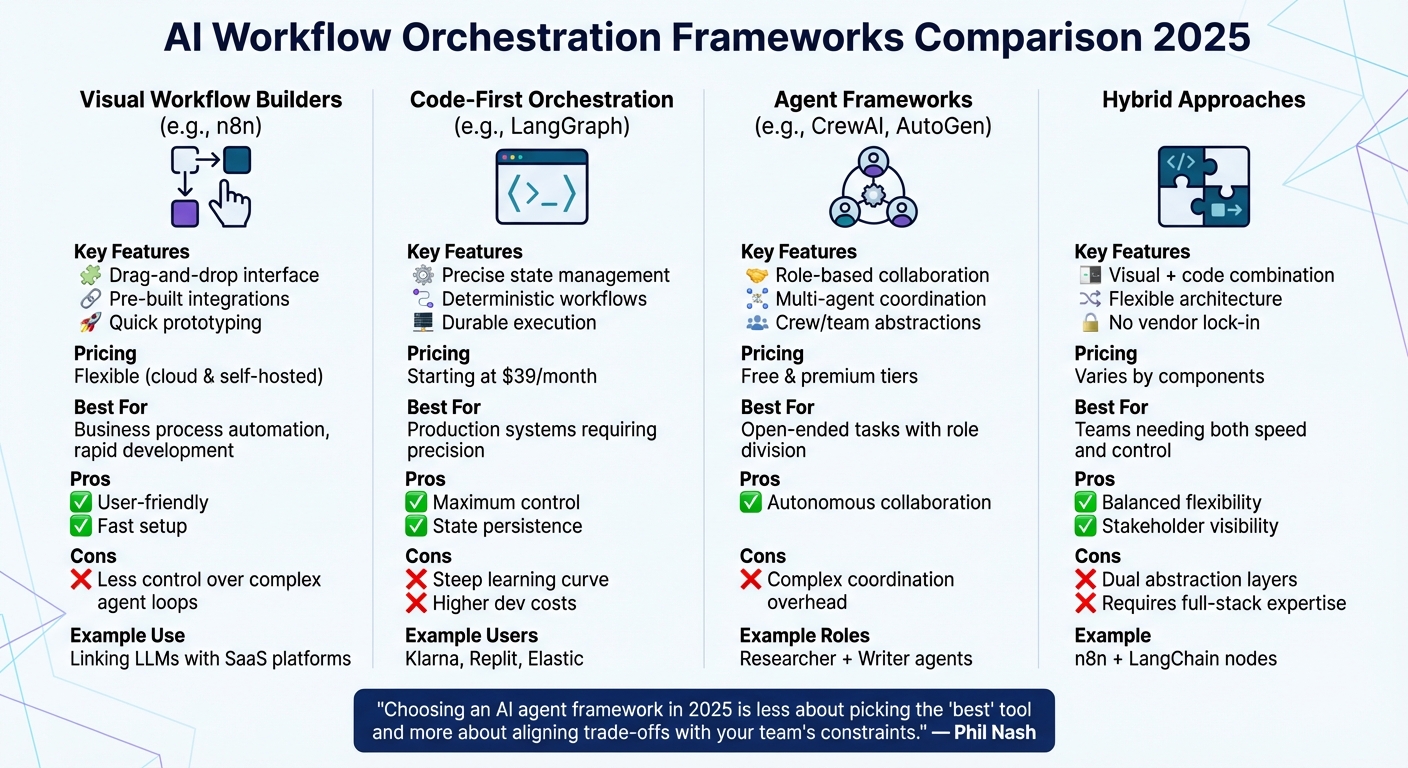
AI Workflow Orchestration Framework Comparison: Visual Builders vs Code-First vs Agent Frameworks
The world of AI workflow orchestration can be divided into four main categories, each catering to different team needs and expertise. Let’s break them down.
Visual workflow builders, like n8n, provide drag-and-drop interfaces and come packed with integrations, making them perfect for quick prototyping and automating business processes. They often offer flexible pricing options, including cloud and self-hosted tiers. These tools shine when it comes to linking large language models (LLMs) with existing SaaS platforms. However, while they’re user-friendly and accessible, they may sacrifice some control over intricate agent loops in favor of speed and simplicity. For teams needing more precision, there are frameworks tailored for developers.
Code-first orchestration frameworks, such as LangGraph, take a developer-centric approach. These frameworks are designed for precise state management and deterministic workflows, while still supporting agentic behavior. Pricing typically starts around $39/month and includes cloud deployment along with observability tools – essential for debugging production systems. Companies like Klarna, Replit, and Elastic rely on LangGraph for its "durable execution" feature, which ensures state persistence during failures and allows for human intervention when needed. While this approach offers unmatched control, it comes with a steep learning curve and higher development costs. For scenarios requiring specialized roles, agent frameworks step in.
Agent frameworks, like CrewAI and AutoGen, focus on role-based collaboration. These frameworks coordinate multiple autonomous agents, such as a "researcher" and a "writer", to tackle open-ended tasks. They use abstractions like "crews" or "teams" to manage hand-offs between agents. Pricing options vary, with both free and premium tiers available. This setup works best for challenges that benefit from clear role division. For teams needing both flexibility and control, hybrid solutions offer a bridge.
Hybrid approaches combine the strengths of visual builders with code-based logic. For example, a team might use n8n to handle API integrations and business logic while embedding LangChain nodes for advanced reasoning tasks. This method avoids vendor lock-in, allowing non-technical team members to visualize workflows while developers retain control over complex state management. However, managing these dual layers of abstraction can be challenging and requires a team with strong full-stack expertise.
"Choosing an AI agent framework in 2025 is less about picking the ‘best’ tool and more about aligning trade-offs with your team’s constraints." – Phil Nash, Developer Advocate, Langflow
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your team’s skills, deployment needs, and whether you’re building a prototype or a robust production system. Visual builders prioritize speed and accessibility for stakeholders. Code-first frameworks provide unmatched precision and deep integration. Agent frameworks excel in autonomous, role-based collaboration. Hybrid models strike a balance, offering flexibility with added complexity. These categories lay the groundwork for creating AI workflows capable of handling execution, validation, and recovery seamlessly.
5 Architecture Patterns That Work
These five patterns tackle common execution challenges, ensuring workflows are efficient, reliable, and ready for production.
Sequential flows use a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure to ensure each step is completed before the next begins. Tools like n8n and LangGraph pass outputs as inputs, maintaining state in a linear sequence. This pattern works best for workflows with clear, step-by-step dependencies – think of processes like "draft, review, polish", where each phase builds on the previous one. Conditional logic acts as a quality gate, verifying each step before moving forward. If validation fails, the workflow loops back for refinement rather than letting errors cascade. This straightforward sequencing is a foundation for more complex patterns like parallel or iterative workflows.
Parallel execution allows independent tasks to run simultaneously, cutting down on overall processing time. Instead of querying multiple data sources one after another, tasks are executed concurrently and their results combined through an aggregator node. In LangGraph, the Send API dynamically generates worker nodes for these parallel tasks, writing outputs to a shared state for later synthesis by the orchestrator. This approach is ideal for tasks like keyword extraction and formatting checks that can occur independently. However, managing shared states can become complicated, and costs can escalate if parallel tasks aren’t properly managed. While this pattern is great for reducing latency, some tasks need iterative refinement, leading us to the next pattern.
Validation loops focus on refining outputs through a cycle of generation, testing, and improvement. Tools like LangGraph enable these loops, which are triggered by validation results. In 2024, Patronus AI introduced Percival, a tool designed for debugging agentic workflows. A case study with Percival revealed over 20 failure modes, increasing accuracy by 60% and cutting debugging time from days to minutes. However, production systems need safeguards – like iteration caps – to avoid infinite loops and excessive API costs. In this setup, one agent generates content while another validates it against quality benchmarks before moving forward.
Human-in-the-loop checkpoints introduce manual approval at critical points to reduce risks in high-stakes scenarios like content moderation, financial transactions, or compliance-sensitive tasks. The workflow pauses, sends the current state to a human reviewer, and resumes only after approval is granted. Both n8n and LangGraph support these checkpoints, offering a balance between automation efficiency and human oversight.
Error handling and fallback logic are essential for maintaining workflow reliability in the face of issues like API timeouts, rate limits, or unexpected responses. Tools like n8n offer logging for failed tasks and configurable retry strategies, while LangGraph’s error handling routes exceptions to predefined fallback paths. By planning for failures, workflows can recover gracefully and maintain production stability.
| Pattern | Best Use Case | Key Benefit | Primary Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sequential Flows | Draft → Review → Polish | Clear, verifiable steps | Error cascades if validation is skipped |
| Parallel Execution | Multi-source research | Faster task completion | Complex state management |
| Validation Loops | Content generation | Improved quality autonomously | High costs without iteration limits |
| Human-in-the-Loop | Financial decisions | Trusted oversight | Potential workflow delays |
| Error Handling | Production reliability | Smooth failure recovery | Risk of overcomplicating simple tasks |
Production Considerations
Prototypes are often created in idealized settings, but taking them to production demands a system that can handle real-world complexities. Without a robust infrastructure that scales effectively, even the most well-planned architecture can fail – especially if costs spiral out of control before you’ve processed your first thousand workflows.
Selecting the right AI orchestration framework is critical for building systems that can thrive in production environments. For more tips on AI workflow engineering, subscribe to our AI Acceleration Newsletter.
Self-Hosting vs. Cloud Deployment
When deciding between self-hosting and cloud deployment, the key tradeoff is data control versus operational convenience. Self-hosted solutions like n8n Community Edition or Langflow give you complete control over data residency. You decide where your data is stored, how it’s processed, and who has access to it. This level of control is particularly important for organizations with strict compliance needs.
Cloud deployments, on the other hand, simplify scaling and offer built-in governance features. Platforms like Azure AI Foundry or Amazon Bedrock handle scaling automatically, reducing the burden of infrastructure management. However, they require sharing data with both model vendors (e.g., OpenAI, Anthropic) and platform providers, which may not align with stringent regulatory requirements.
The choice boils down to priorities. A self-hosted setup demands more engineering effort but allows flexibility to switch model providers without a major overhaul. Cloud platforms ease infrastructure management but increase dependency on third-party services. Once you’ve chosen your deployment strategy, the next step is managing costs effectively.
Cost Modeling and Budgeting
A clear understanding of your cost structure is essential to avoid budget surprises. Cloud-native services typically charge per token or per session, making costs unpredictable as workflows grow more complex. For teams with steady usage patterns, flat-rate subscriptions – like n8n Cloud at $24/month for 2,500 executions or Flowise Cloud at $35/month for 10,000 predictions – can provide more stable budgeting.
Consider the example of Direct Mortgage Corp., which, in May 2025, implemented a multi-agent system with specialized "Document AI" and "Decision AI" agents. By routing tasks to smaller, cost-efficient models instead of relying on a single, expensive model, they cut loan-processing costs by 80% and accelerated application approvals by 20 times. Amazon Bedrock’s Nova Micro model, for instance, costs just $0.000035 per 1,000 input tokens, making it an economical choice for high-volume tasks.
Don’t forget to account for additional expenses like vector database storage, API calls, and observability tools. While self-hosting eliminates managed service fees, it introduces direct infrastructure costs that need to be factored into your budget.
"The advantage of having a single control plane is that architecturally, you as a data team aren’t paying 50 different vendors for 50 different compute clusters, all of which cost time and money to maintain." – Hugo Lu, CEO, Orchestra
After setting your deployment and cost strategies, the next critical step is ensuring system reliability through debugging and observability.
Debugging and Observability
Production systems encounter failures that prototypes never face. Tools like LangSmith and LangFuse have become go-to solutions for tracking requests, evaluating outputs, and monitoring deployments. They even break down token costs by specific agents, helping you spot and fix "token-hungry" loops before they become a problem. For multi-node sequences, n8n offers detailed execution logs and run histories, making it easier to pinpoint failures.
LangGraph takes debugging a step further with its "time travel" feature, allowing you to inspect, pause, and modify agent states at any point in execution. This is invaluable when troubleshooting complex workflows. To avoid future headaches, integrate observability from the start. Collecting operational data early helps establish performance baselines, detect anomalies, and optimize your system over time.
Version Control for Workflows
Version control isn’t just for code – it’s essential for workflow updates too. Breaking changes in production workflows can be costly, so tools like n8n and Langflow allow you to export workflows as JSON files, which can then be tracked in Git repositories. This approach works well for teams that prefer visual interfaces but still need versioning discipline. Code-first frameworks like LangGraph treat workflow definitions as source code, with native Git support for branching, merging, and rollbacks.
Another best practice is separating prompt management from your core workflow logic. By externalizing prompts, you can tweak agent behavior without redeploying the entire workflow. This separation also makes A/B testing more straightforward – you can test prompt variations against historical datasets using automated evaluation tools like Evals before rolling out changes. Version control isn’t just about avoiding mistakes; it’s about enabling confident and efficient iteration.
sbb-itb-32a2de3
4 Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many AI workflow failures can be traced back to four recurring mistakes. These issues crop up in teams of all sizes, from startups to massive enterprises, and they’re much easier to prevent upfront than to untangle after deployment.
Over-Engineering Simple Tasks
Overcomplicating straightforward tasks can lead to unnecessary headaches. For instance, a single API call often outperforms a complex multi-agent system for basic workflows. Adding extra tools or writing overly long system prompts may seem like a good idea, but it often backfires. As token usage rises, you’ll need more advanced (and expensive) models just to handle the added complexity.
Here’s the kicker: token costs can balloon quickly. While a standard chat interaction uses a baseline amount of tokens, AI agents might consume four times more. Multi-agent systems? They can spike up to 15 times due to recursive reasoning loops. These loops can spiral into error cascades and unstable memory, making debugging a nightmare.
The solution? Stick to the KISS principle (Keep it Simple, Stupid). Design agents to handle specific tasks instead of trying to create one that does it all. For predictable processes like document translation or content verification, opt for straightforward solutions like prompt chaining. Tools like n8n ($24/month for 2,500 executions) are a great fit for simple automations. More advanced frameworks like LangGraph (starting at $39/month) should only be used when you need deep, stateful control.
While over-engineering is one pitfall, failing to properly secure critical workflows is another.
Under-Engineering Critical Paths
For high-priority workflows, skipping error handling and validation is a recipe for disaster. These workflows often follow a critical path – the sequence of tasks that must be completed without delay. In AI projects, this might look like: data collection → preprocessing → model training → validation → deployment. If any one of these steps falters, the entire timeline is thrown off.
Critical paths require robust safeguards. Without them, a single error can send an AI agent into a loop of flawed reasoning, leading to "out of token" errors or skyrocketing API bills. A good example of getting it right? In 2024, Boston Consulting Group helped a shipbuilding firm cut engineering effort by 45% using a multi-agent design system. They succeeded by focusing on high-stakes, low-volume decisions where accuracy mattered more than compute costs.
To avoid pitfalls, use the Critical Path Method (CPM) to map out task sequences and identify steps with no slack time. These should get top priority for error handling and resource allocation. Set strict limits on agent iterations and token usage. For regulated or frequent tasks, structured workflows offer better traceability and cost predictability. Adding XML tags like <Task> or <Guardrails> in prompts can help large language models (LLMs) process instructions more efficiently and reduce errors.
Ignoring Error States
APIs can fail, timeout, or return unexpected data – it’s inevitable. Without fallback strategies, workflows crumble when external services hit a snag. Companies that implement proper error handling report up to 4.8 times higher productivity and 49% fewer errors.
Fallback strategies are a must for critical workflows. This includes setting up validation rules, retry mechanisms, and automated recovery options to handle failures. For instance, you might route tasks to alternative agents or gracefully shut down a workflow when something breaks. Another option? Build “maker-checker” loops where one agent generates an output and another reviews it. For especially critical decisions, human-in-the-loop checkpoints can add an extra layer of security.
"AI should enhance – not replace – human input. Design workflows where AI handles routine tasks and real-time data analysis, while your team focuses on higher-value work and decision making. Maintain manual review points for critical steps or exceptions." – Alex Zhezherau, Product Director, Wrike
While error handling is key, neglecting performance tracking can leave you blind to problems until they escalate.
Building Without Measurement
You can’t fix what you can’t measure. Observability tools help track execution times, success rates, and costs, making it easier to spot inefficiencies and optimize performance. Without these metrics, hidden issues can fester until they cause major disruptions. Real-time monitoring can catch problems like "data drift" or performance drops early, allowing for quick fixes.
Despite its importance, measurement often gets overlooked. While 79% of companies are adopting AI agents, only 1% describe their implementations as "mature." Why? A lack of infrastructure for observability and fallback systems is a common culprit.
Tracking both technical and business KPIs – like error rates, response times, conversion rates, and ROI – provides a well-rounded view of AI performance. Regular audits and validation checks can catch issues before they spiral out of control. Predictive analytics can even act as an early warning system, flagging potential problems based on historical data.
"Measuring AI performance requires multiple metrics. To properly evaluate AI, companies need to use a mix of business, technical, and fairness metrics." – Neontri
Conclusion
The tools you select – whether it’s n8n, LangChain, or another framework – lay the groundwork for your AI workflows. However, it’s your architecture patterns that ultimately decide if those workflows can scale effectively and operate reliably. Key elements like sequential flows, parallel execution, validation loops, and robust error handling are what separate a dependable system from one that falters under pressure.
These architecture patterns are the backbone of reliable AI systems. Which orchestration pattern aligns best with your needs? Consider subscribing to our AI Acceleration Newsletter for weekly updates on building scalable, production-ready AI solutions.
"Orchestration is no longer optional – it’s the foundation for making AI useful, observable, and dependable." – Hugo Lu, CEO, Orchestra
In May 2025, a standout case demonstrated how selecting the right architecture pattern significantly reduced costs and sped up application approvals. The right choice can make all the difference.
If you’re a technical founder looking to implement these principles in practical systems, consider joining Elite Founders. You’ll have the chance to workshop your architecture with experienced practitioners who design these systems daily. These sessions provide live demonstrations and actionable strategies, ensuring you walk away with a system ready to deploy.
FAQs
What are the advantages of using hybrid approaches for AI workflow orchestration?
Hybrid approaches bring together the simplicity of visual, no-code tools and the precision of code-first frameworks, creating a powerful combination. With drag-and-drop interfaces, you can quickly prototype workflows while still having the option to integrate custom scripts or nodes for more intricate tasks, unique logic, or handling edge cases. This approach speeds up development while maintaining a high level of control.
These platforms support advanced execution patterns like parallel processing, conditional flows, and validation loops, which help build scalable and efficient systems. They also include built-in tools for debugging, observability, and versioning, cutting down on operational headaches. This adaptability empowers engineers to design workflows that are not only reliable but also flexible, making it easier to move from initial prototypes to fully functional, production-ready systems.
Should I choose self-hosting or cloud deployment for my AI workflows?
Deciding whether to go with self-hosting or cloud deployment comes down to factors like data control, budget, and operational resources. If your operations involve handling sensitive information or adhering to strict regulations such as HIPAA or GDPR, self-hosting gives you full control over your data and infrastructure. It also offers more predictable costs – provided you have the expertise and resources to effectively manage your hardware and systems. That said, self-hosting demands a skilled team to handle responsibilities like server maintenance, scaling, and performance monitoring.
On the flip side, cloud deployment works best for teams that value speed, scalability, and convenience. By choosing the cloud, you can skip the hassle of managing infrastructure. Many cloud platforms come with built-in tools for monitoring, debugging, and scaling, making it easier to handle fluctuating workloads. However, cloud solutions can bring challenges like vendor lock-in and variable costs. Despite that, they’re often the go-to option for teams working on fast-paced projects or those dealing with unpredictable demand.
In short, if you’re managing compliance-heavy workflows with consistent demand, self-hosting might be the better fit. But for agile projects or workloads that change frequently, cloud deployment offers the flexibility and simplicity to keep things moving.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when designing AI workflows?
When building AI workflows, avoiding certain pitfalls can make all the difference in ensuring efficiency and reliability. One of the most frequent missteps is over-engineering tasks that should remain simple. Adding layers of unnecessary complexity not only slows down development but also makes ongoing maintenance a headache. At the other end of the spectrum, under-engineering critical components can result in systems that crumble under pressure, especially when faced with real-world challenges.
Another major issue is overlooking error handling and fallback mechanisms. AI workflows must be prepared for hiccups – whether it’s an API failure or some unexpected input – and should include strategies to manage these situations gracefully. Lastly, skipping measurement and observability can leave you flying blind. Without proper tools to monitor performance, debug problems, or fine-tune workflows, it becomes nearly impossible to ensure long-term success. Integrating monitoring and metrics right from the start is a must.